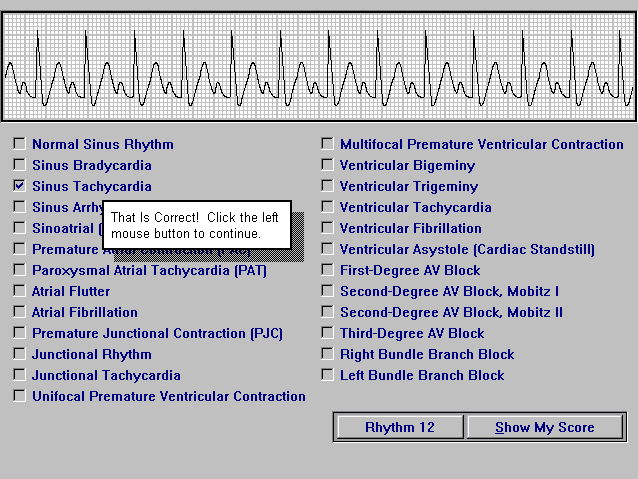
いろいろ sinus rhythm with multifocal pjc 580128-Sinus rhythm with multifocal pvc couplet
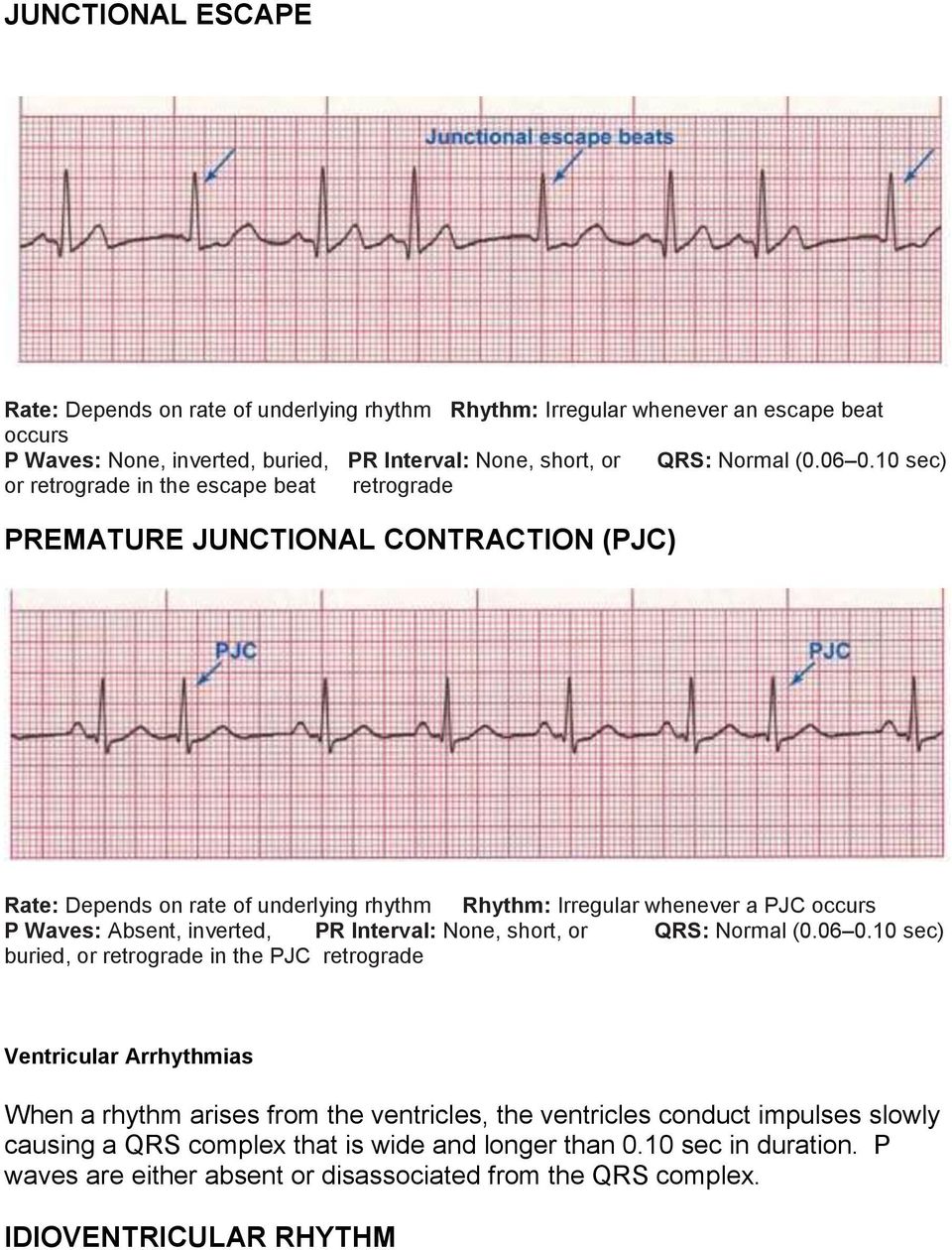
Junctional ( escape) Rhythm 4060 bpm Normal Sinus Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Second Degree AV Block, Type 2 PR interval becomes progressively longer , until a P wave occurs without a QRS complex , after the pause the PR interval cycle starts again irregular treatment atropine or pacemaker Second Degree AV Block, Type 2Dec 02, 15Ventricular arrhythmias included premature ventricular complexes (PVCs) in 434%, >0 PVCs per 24 hours in 33%, multifocal PVCs in 53%, nonsustained ventricular tachycardia in 07%, and accelerated idioventricular rhythm in 03% Bradyarrhythmias included sinus pause >3 seconds in 03%, and seconddegree AV block in 24%Jun 13, 16The sinus P waves of the underlying rhythm can be seen just before the PVC in example A and after the PVC in the ST segment in example B These P waves are associated with the underlying rhythm (not the PVC) and usually are hidden within the wide QRS of the premature ventricular contraction
Lesson V Ecg Rhythm Abnormalities
Sinus rhythm with multifocal pvc couplet
Sinus rhythm with multifocal pvc couplet-I Sinus rhythms and arrhythmias A Records the impulse originating from the sinus node and follows the path to the atria, AV junction, and through the bundle of His, to the bundle branches and on to the Purkinje fibers B Sinus node is the main pacemaker C Sinus rhythms include 1 Normal sinus rhythm 2 Sinus tachycardia 3 SinusImages These are the images used in this course Click on any of the thumbnails to enlarge the image EKG Holter Monitor Schematic diagram of normal sinus rhythm for a human heart as seen on ECG Figure 11 Electrical cells and mechanical cells Figure 12



1
Mar , 21PVC marked by the arrow on an EKG in sinus rhythm The compensatory pause is marked in blue The ectopic impulses on the electrocardiogram are premature in relation to the expected impulse of the basic rhythm The QRS complex is abnormal in duration and morphologyCardiac Rhythm or Arrhythmia Rates/Ratios Ectopic Activity Available;Normal Sinus Rhythm 60, 80, 100 Sinus Bradycardia
Mar , 21Ventricular Escape Rhythm or Idioventricular Rhythm Ventricular escape rhythm or idioventricular rhythm occurs in the absence of supraventricular stimuli or with bradycardias with heart rate below 40 bpm (sick sinus syndrome or complete AV block distal to the bundle of His) 3Ventricular escape rhythm is observed on the electrocardiogram as a slow, regular rhythmMay 09, 13Nice, clear example of ventricular bigeminy with an underlying sinus rhythm We do not know from this strip if the sinus rhythm is a bradycardia at a rate of about 42 per minute, or if the underlying sinus rhythm is actually at a rate of 85 per minute, with every other sinus beat inhibited by the occurance of a PVCNormal Sinus Rhythm with multifocal PVCs Normal sinus rhythm with unifocal PVCs Which rhythm is this?
PAC PJC Unifocal PVC Multifocal PVC Couplet PVC;Depending whether there are one, two, or three normal beats between each PVC, the rhythm is called bigeminy, trigeminy, or quadrigeminy If 3 or more PVCs occur in a row it may be called ventricular tachycardia The precise shape of the QRS can give an indication as to where precisely in the heart muscle the abnormal electrical activity arisesJan 02, 18Normal sinus rhythm Normal sinus rhythm is defined as the rhythm of a healthy heart It means the electrical impulse from your sinus node is being properly transmitted In adults, normal sinus



Electrocardiography Part Ii Download Educational Software For Electrocardiography Technicians And Ecg Ekg Students




Premature Supraventricular Complexes Basic And Bedside Electrocardiography 1st Edition 09
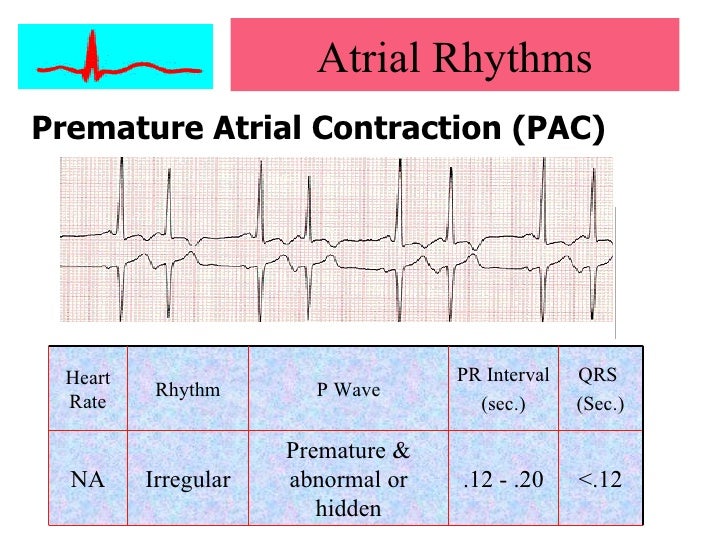
PVC's may be unifocal (from one spot on the ventricle wall) or they may be multifocal (from two or more different spots foci on the ventricle wall) Obviously, the multifocal PVC is the more dangerous condition;Ectopic atrial rhythm is similar to ectopic atrial tachycardia, but with HR <Sinus Rhythm Types The dysrhythmias in this category occur as a result of influences on the Sinoatrial (SA) node Rhythms in this category will share similarities in a normal appearing P wave, the PR interval will measure in the "normal range" of 012 – 0 second, and the QRS typically will measure in the "normal range" of 006 – 010 second



2



Lesson V Ecg Rhythm Abnormalities
Jun 03, 13PVCs are probably the second most common rhythm problem I see Atrial arrhythmia, including AF and atrial flutter are the most common This image shows PVCs (beats 2, 4, 6 etc) occurring in what we call a bigeminal pattern Atrial or ventricular beats that appear in an every other beat pattern are referred to as bigeminy Dr22 Sinus Rhythm with Unifocal PVCs (3 &Sinus Rhythm W/ PVC M Sinus Rhythm W/ multifocal PVC'S N Monomorphic VTach O 8 Poly VTach P Poly VTach / Torsades de points ( prolong QT) Q Poly VTach / Torsades de points R 9 Fine Vfib S Coarse Vfib T Coarse Vfib that converts to Asystole after defibrillation U 10



By The End Of This Continuing Education Module The Clinician Will Be Able To Pdf Free Download




Ecg Educator Blog Premature Junctional Complex Pjc
Aug 01, However, if an ectopic focus depolarises early enough — before the arrival of the next sinus impulse — it may "capture" the ventricles, producing a premature contraction Premature contractions ("ectopics") are classified by their origin — atrial (PACs), junctional (PJCs) or ventricular (PVCs)May 19, 16PVC Practice Strips (class 6) 01 Identify the following rhythm a Sinus rhythm with multiform PVCs b Sinus bradycardia with a trigeminal PVCs d Sinus tachycardia with uniform PVCsDescription, management and treatment of sinus rhythm with multifocal pvc's A A A Close Heart Rhythm Community 122k Members description, management and treatment of sinus rhythm with multifocal pvc's chryzdhell just want to know about the ecg decription of an ecg strip revealing a SINUS RHYTHM WITH



Ekg Rhythm Identification




Ectopic Complexes And Rhythms Thoracic Key
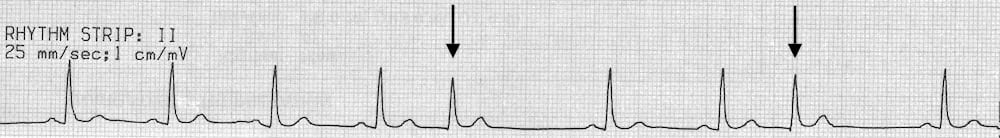
Aug 01, Multifocal PVCs Sinus rhythm with PVCs of two different morphologies (arrows) Note the appropriately discordant ST segments / T waves The pause surrounding the PVC is equal to double the preceding RR interval (= a full compensatory pause)Rhythm analysis indicates sinus tachycardia at over 100 bpm First degree heart block is also present This encounter shows a fast rate over 100 bpm, with a regular rhythm and P waves, indicating sinus tachycardia The extremely long delay between the P wave and QRS indicates first degree heart blockAug 15, The ECG criteria to diagnose premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) is discussed with 12lead ECG examples including ventricular bigeminy



Cardiac Arrhythmias




Ectopic Complexes And Rhythms Thoracic Key
It is perfectly appropriate to call this something very descriptive like "sinus tachycardia with a unifocal PVC every third beat", but this rhythm is often called sinus tachycardia with ventricular trigeminy If every second complex was a PVC, it can be called bigeminyPremature atrial complex with noncompensatory pause Premature atrial complexesFeb 24, 18View Test Prep quizlet EKGpdf from NURS DDD at Baptist Health College Little Rock Atrial Flutter First Degree AV Block Junctional Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Normal Sinus Rhythm Second Degree AV




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography



1
Ectopic atrial rhythm is similar to ectopic atrial tachycardia, but with HR <Your heart's normal, or sinus, rhythm is controlled by a natural pacemaker, the sinus node, which creates electrical impulses that travel across the atria to the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood out to your lungs and body in what is known as normal sinus rhythm PVCs occur when ventricle contractions beat sooner than the next expected regular heartbeat, oftenNormal Sinus Rhythm with unifocal PVCs Premature atrial complex with noncompensatory pause Which rhythm is this?




Practice Test Only Dysrhythmia Interpretation Therapeutic Modalities Pdf Free Download



Ekg Rhythm Identification
Aug 06, 16Sinus rhythm with a triplet and couplet of PVCs Sinus rhythm with a triplet and couplet of PVCs Posted by Unknown at 0300 Email ThisBlogThis!Share to TwitterShare to FacebookShare to Labels Couplet , TripletThe next sinus beat will occur one sinus cycle after resetting the sinoatrial node The pause will be less than compensatory and the retrograde Pwave is often visible on the STTsegment Ventricular echo This is a rare phenomenon in which the impulse from the PVC is conducted through the atrioventricular node and there it circulates back toSinus rhythm = normal heart rate and rhythm Heart Rhythm Society Public &




What Are Premature Atrial Contractions Patmac Rn




Bigeminy Wikipedia
Various Rhythms with Multifocal PVCs 1 Normal Sinus Rhythm with Multifocal PVCs 2 Atrial Flutter with Multifocal PVCs 3 Normal Sinus Rhythm with Multifocal PVCs 4 Normal sinus rhythm with multifocal PVCsAll of my EKG's have been normal except for one that showed sinus arrhythmia and one that had a PAC I have had 3 echos, three 24 hour monitors, and a stress test The most recent testing was in May My heart seems to be getting worse and worse since then with PAC's and PVC's and now this sinus arrhythmiaPatient Information Center Heart Block Types of Heart Block Firstdegree heart block (also called firstdegree AV block) The electrical impulses are slowed as they pass through the conduction system, but all of them successfully reach the ventricles



1




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography
Try to figure out whether that beat is a premature atrial contraction, premature ventricular contraction, etcIdioventricular rhythm (22) Junctional Rhythm (8) Junctional Rhythms (58) LVAD (1) Maternal cardiac arrest (1) Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (7) Multifocal PVCs (2) Nonconducted P waves (2) Nonconducted PACs (2) Normal Sinus Rhythm (1) NSTEMI (10) Nurse (21) Nursing Stuff (41) Overdrive pacing (1) P wave Asystole (4) Paced rhythms (17) PACs (2Rhythm analysis indicates normal sinus rhythm (NSR) at 68 bpm Premature atrial complexes (PACs), Premature junctional complexes (PJCs), and Premature ventricular contractions (PVCs) are present This encounter shows a normal sinus rhythm with a large amount of ectopy



Ekg Basics Bingo Card




Ekg Rhythms From Order To Chaos
Oct 19, 16The sinus node creates electrical impulses that travel across the atria to the ventricles, causing them to contract and pump blood out to your lungs and body in what is known as normal sinus rhythm In the case of PVCs, the heart doesn't actually skip a beat Instead, an extra beat comes sooner than normalNov 14, 16Multifocal PVCs all look different from each other on the same ECG They occur at different intervals, at various times in the QRS cycle, with different coupling intervals Multiformed PVCs usually have the same coupling intervals (because they originate in the same ectopic site but their conduction through the ventricles differMar 09, 16Normal Sinus Rhythm with Multifocal PVC'S B Normal Sinus Rhythm with Unifocal PVC'S C Normal Sinus Rhythm with PAC'S D Normal Sinus Rhythm with PJC'S 6 Name this strip A Normal Sinus Rhythm with PJC'S B Normal Sinus Rhythm with PAC'S C Normal Sinus with PVC'S D



Ekg Rhythms Interpretation Best Practice Quiz Strips Acls




Advanced Assessment Ecg Interpretation Version 14 Obhg Education
PVC 80 NSR with Multifocal PVCs Coupl PVC 80 Sinus with Coupled PVCs PAC 80 Sinus with PACs (Premature Atrial Complex) PJC 80 Sinus with PJCs is the Normal Sinus Rhythm (NSR) 423 Selecting a New Rhythm To select a new rhythm simply press the key of the new rhythm you require Your new selection is indicated as a waiting rhythmFeb 26, 18This is known as a premature ventricular complex (PVC) or ventricular premature beat When this occurs in a threebeat pattern, doctors call itMay 27, 16 d Sinus rhythm with multifocal PVCs 21 d Sinus rhythm with PACs 22 d Sinus rhythm with PACs 23 e a Sinus tachycardia 24 c Atrial fibrillation with slow ventricular response 25 d Sinus rhythm with bigeminal PACs 26 a Atrial flutter 27 d Atrial flutter 28 e Normal sinus rhythm 29 a Sinus arrhythmia 30 b Supraventricular
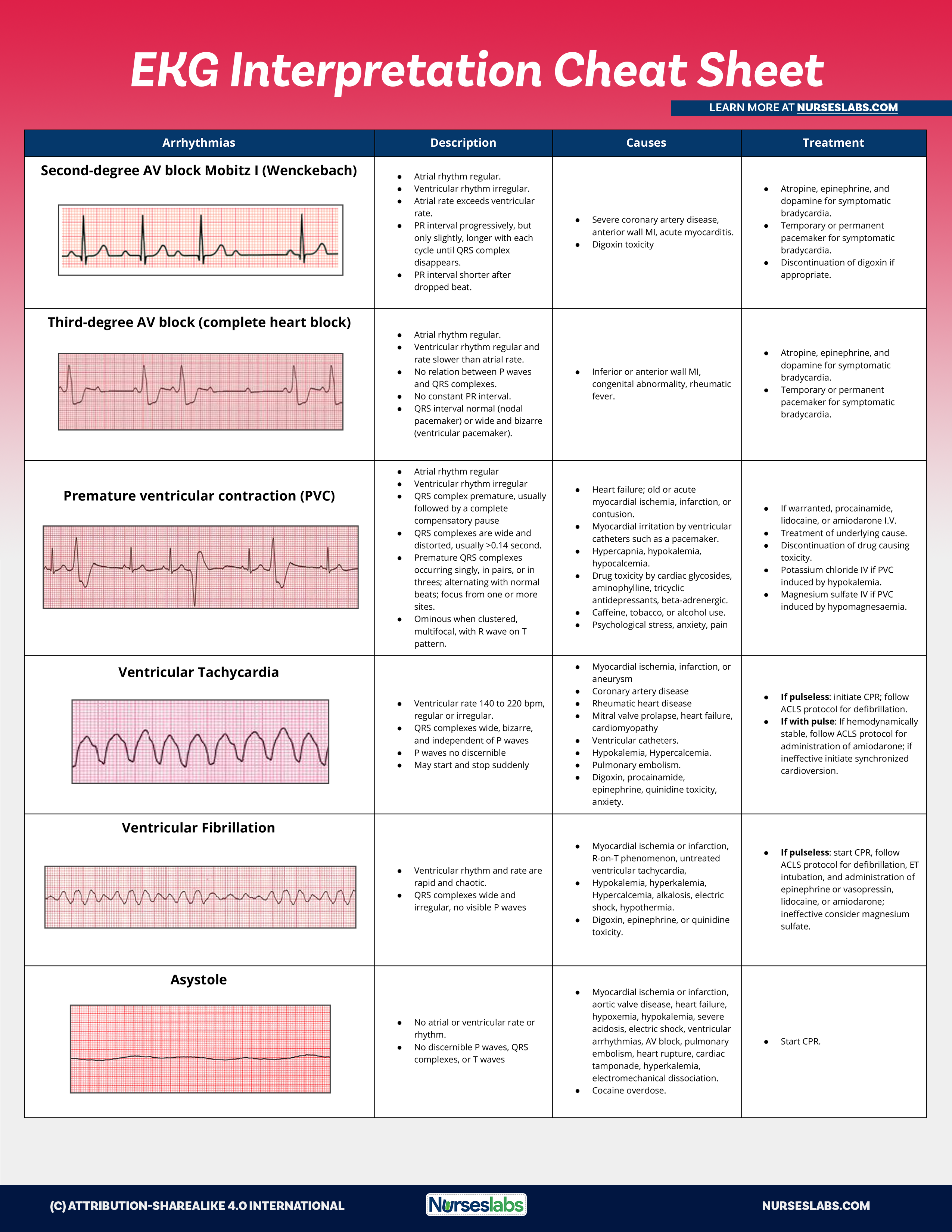



Ekg Interpretation Cheat Sheet Heart Arrhythmias Guide Update




Premature Junctional Contractions
It indicates the general irritability of the myocardium and the possibility of even more dangerous heart arrhythmiasA) Sinus rhythm with a PVC b) Sinus rhythm with a PAC c) Accelerated junctional rhythm with a PVC d) Junctional tachycardia with a PVC Answer c) Accelerated junctional rhythm with a PVC Explanation The underlying ECG rhythm includes narrow QRS complexes, no P waves and a rate of about 80/minute This rhythm originates from the AVBigeminy is a cardiac arrythmia in which there is a single ectopic beat, or irregular heartbeat, following each regular heartbeatMost often this is due to ectopic beats occurring so frequently that there is one after each sinus beat, or normal heartbeatThe two beats are figuratively similar to two twins (hence bi gemini)For example, in ventricular bigeminy, a sinus beat is shortly




Multifocal Premature Ventricular Contractions Pvcs Youtube
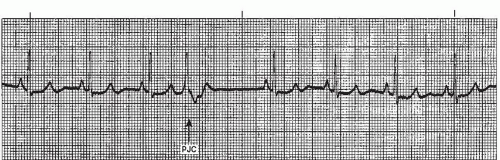



Junctional Arrhythmias And Av Blocks Thoracic Key
100 bpm Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) and rhythm Discrete, multifocal P' waves occurring at rates of /min and with varying P'R intervals (should see at least 3 different P wave morphologies in aInterpretation of the rhythm displayed is Interpretation of the rhythm displayed is Ventricular fibrillation Sinus rhythm with multifocal PVCs6) Could be Ventricular Trigeminiy 23 Atrial Fibrillation rate of 90 (irregular with no discernable P waves) 24 Second Degree AV Block Type I (Wenchebach) PR longer, longer, dropped beat 25 Sinus Rhythm with multifocal PVC's




Authetic Basic Ecg Rhythms Poster




Ekg Medic Rhythms Atrial And Vent Flashcards Quizlet
Group 2 Escape (late) beats and premature (early) beats The bottom line for Group 2 arrhythmias is that the rhythm is fairly regular then you will notice an early or late beat;Jan 05, The rhythm is indeed irregularly irregular, so atrial fibrillation must be considered There are 5 other rhythms that are irregularly irregular, though atrial fibrillation is by far the most common 1 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia 2 Sinus with multifocal PACs 3 Sinus with multifocal PVCsJun 18, 17c Sinus rhythm with bigeminal premature ventricular contractions d Sinus rhythm with paired premature ventricular contractions (couplets) ANS C A single ectopic focus produces PVC waveforms that look alike, called unifocal PVCs Waveforms of PVCs arising from multiple foci are not identical and are called multifocal PVCs PVCs may occur in a predictable pattern, such



2




Introduction To Telemetry Monitoring For Arrhythmias Nursing Ce Course Nursingce
100 bpm 6 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia (MAT) and rhythm Discrete, multifocal P' waves occurring at rates of /min and with varying P'R intervals (should see at least 3 different P wave morphologies in a
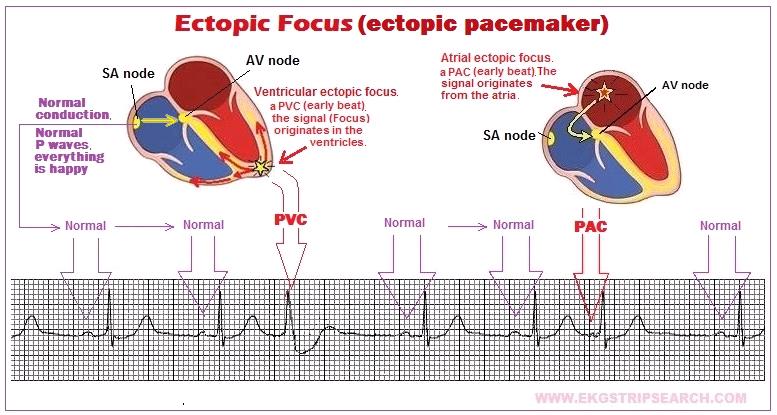



Ectopic Focus



Premature Atrial Complex Pac Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis



Section 10 Premature Complexes
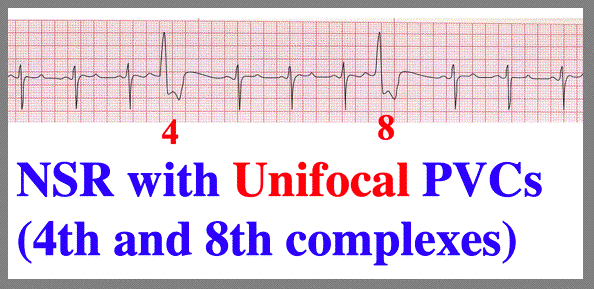



More Pvc Configurations




Premature Supraventricular Complexes Basic And Bedside Electrocardiography 1st Edition 09




Ecg Examples A Sinus Rhythm With Multifocal Premature Ventricular Download Scientific Diagram




Float Nurse Ekg Quiz 336



2



Ekg Rhythm Identification



2




Ekg Medic Rhythms Atrial And Vent Flashcards Quizlet




The Six Second Ecg Squarespace Pages 1 6 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5




Basic Arrhythmia Handout Oakwood Healthcare System



Online Module 8 Quiz Proprofs Quiz



Ecg Rhythm Review Scope




Premature Supraventricular Complexes Basic And Bedside Electrocardiography 1st Edition 09




How To Calculate Heart Rate From Ecg Arxiusarquitectura
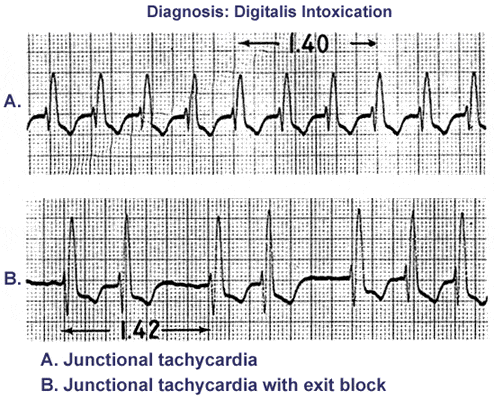



Av Junctional Arrhythmia Junctional Premature Complex Junctional Tachycardia 네이버 블로그



Ekg Basics Bingo Card



Premature Junctional Complex Pjc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




Dysrhythmia Interpretation And Management Ppt Download



Premature Ventricular Complex Pvc Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis




What Types Of Pathology Can We Identify And




Introduction To Cardiac Rhythm Analysis
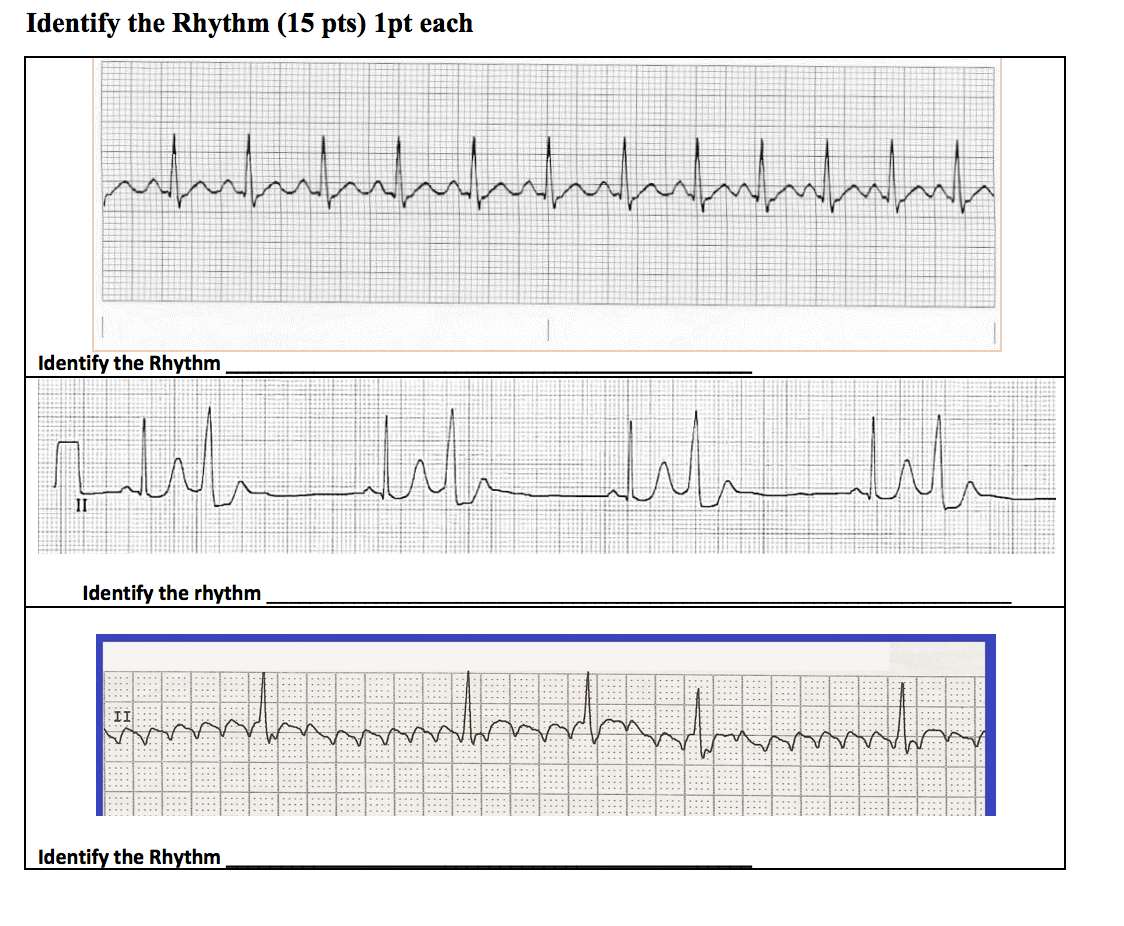



Only Use The Options Provided Answers May Be Used Chegg Com




Ecg Rhythms Sinus Rhythm With Long Pri Mimicking Junctional Rhythm




Ekg Interpretation Cheat Sheet Heart Arrhythmias Guide Update



1




Premature Atrial Contraction Pac The Premier Ekg Resource For Medical Professionals Ekg Md Dr Anthony Kashou
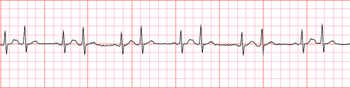



Bigeminy Wikipedia




Ecg Rhythm Review Scope




Introduction To Cardiac Rhythm Analysis
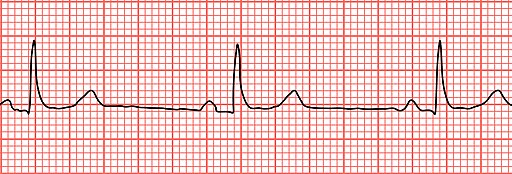



Conduction Disorders Pearls Smarty Pance




Pac Pjc Pvc Pdf 5 Minute Speedy Session Telemetry Pac Pjc Pvc Sinus Rhythm Just A Baseline To Compare To The Other Strips Notice That Every P Wave Has Course Hero



2



2



Basic Electrocardiography Guide To Diagnostic Tests



2
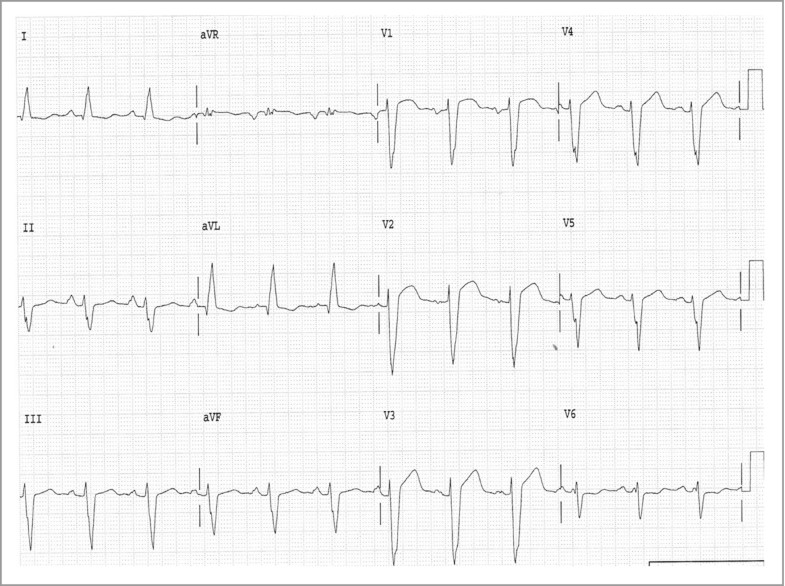



Electrocardiography Springerlink



2




Advanced Assessment Ecg Interpretation Version 14 Obhg Education
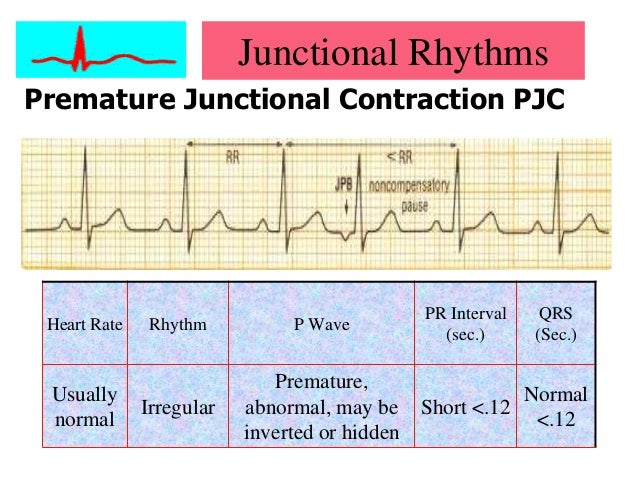



Cardiac Arrythmias




Ecg Rhythms Several Tricks Of A Pjc In One Strip



2




Ecg Learning Center An Introduction To Clinical Electrocardiography



2




Pdf Arrhythmias In Children And Young Adults
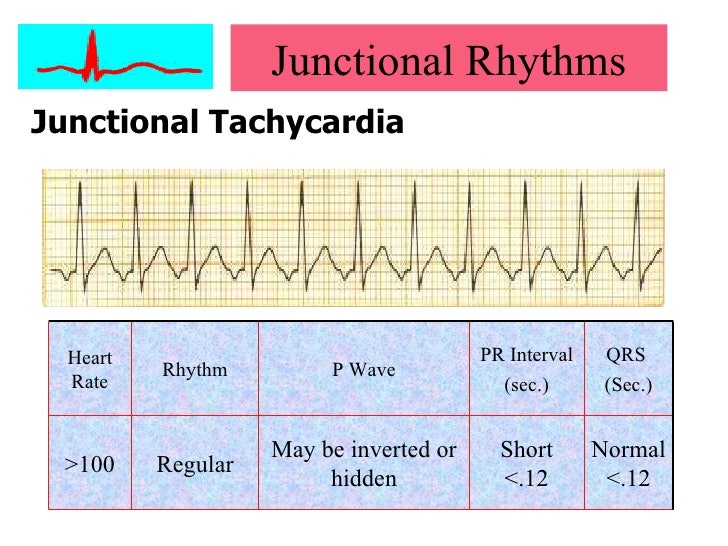



Av Junctional Arrhythmia Junctional Premature Complex Junctional Tachycardia 네이버 블로그



What Happened Ems 12 Lead



Electrocardiography Part Ii Screen Shots




Float Nurse Ekg Rhythm Strip Quiz 50
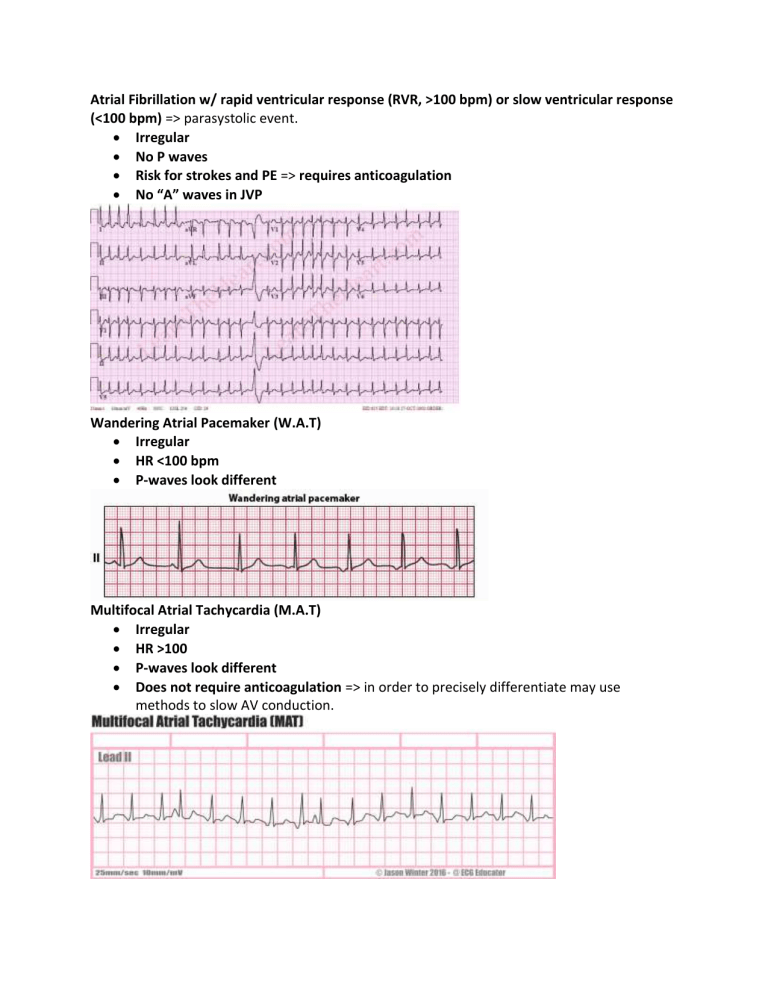



Medcram Ekg Course




Ecgrhythms Multifocal Atrial Arrhythmia Ecg Recognition T Co Quiekrsynw Twitter
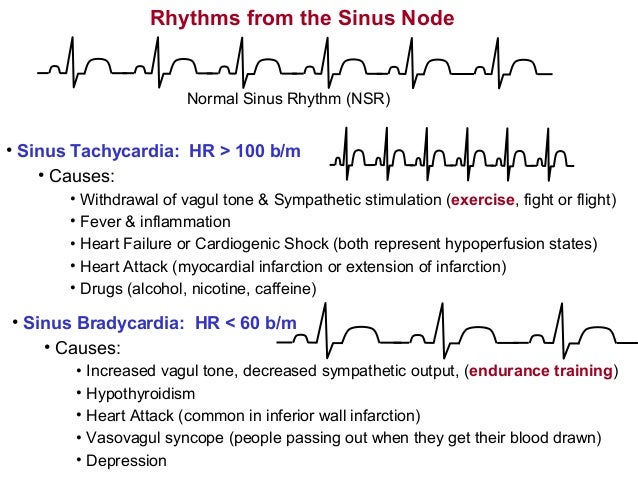



Arrhythmias19



Lesson V Ecg Rhythm Abnormalities




Ekg Flashcards Quizlet




Pac Pjc Pvc Pdf 5 Minute Speedy Session Telemetry Pac Pjc Pvc Sinus Rhythm Just A Baseline To Compare To The Other Strips Notice That Every P Wave Has Course Hero




Ekg S By Robby Zehrung Leads In A 3 Lead View There Are Two Types Of Leads Bipolar Lead I Right Arm To Left Arm Lead Ii Right Arm To Left Ppt Download
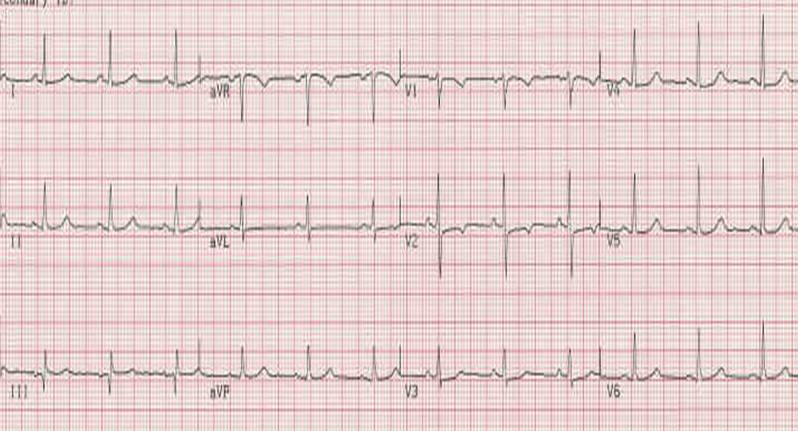



Electrocardiography Wikidoc



1
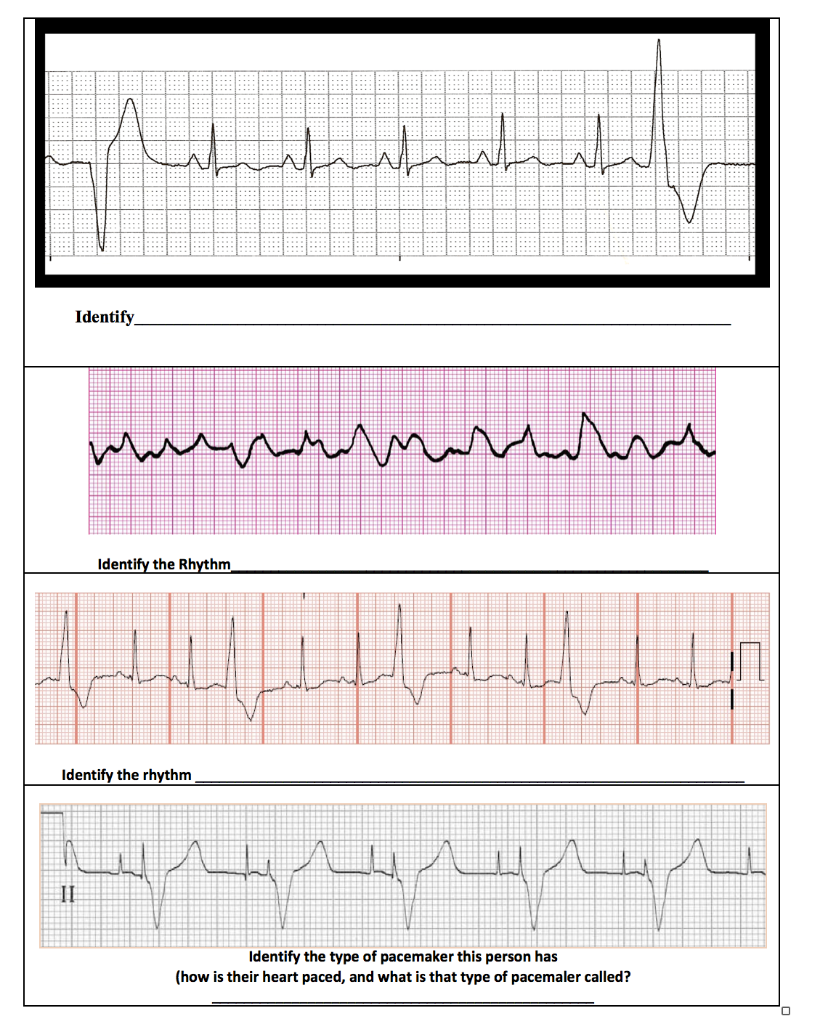



Only Use The Options Provided Answers May Be Used Chegg Com




Sage Books Acute Illness Management
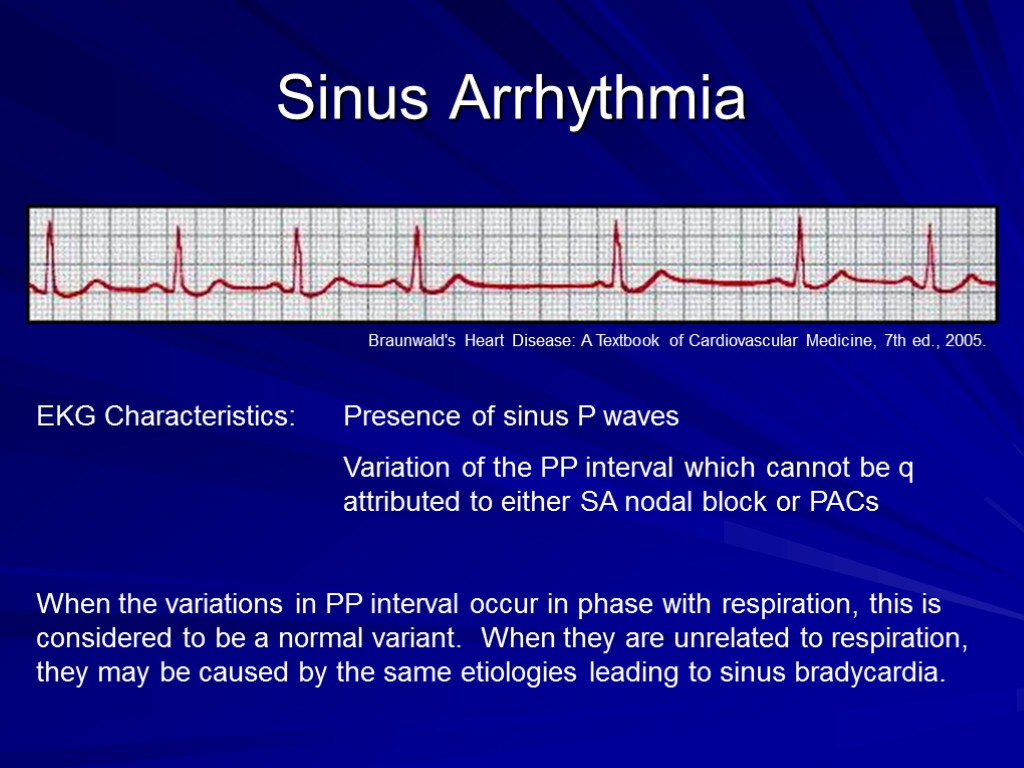



Arrhythmias And Ekgs Part 2 Outline Sinus Arrhythmia
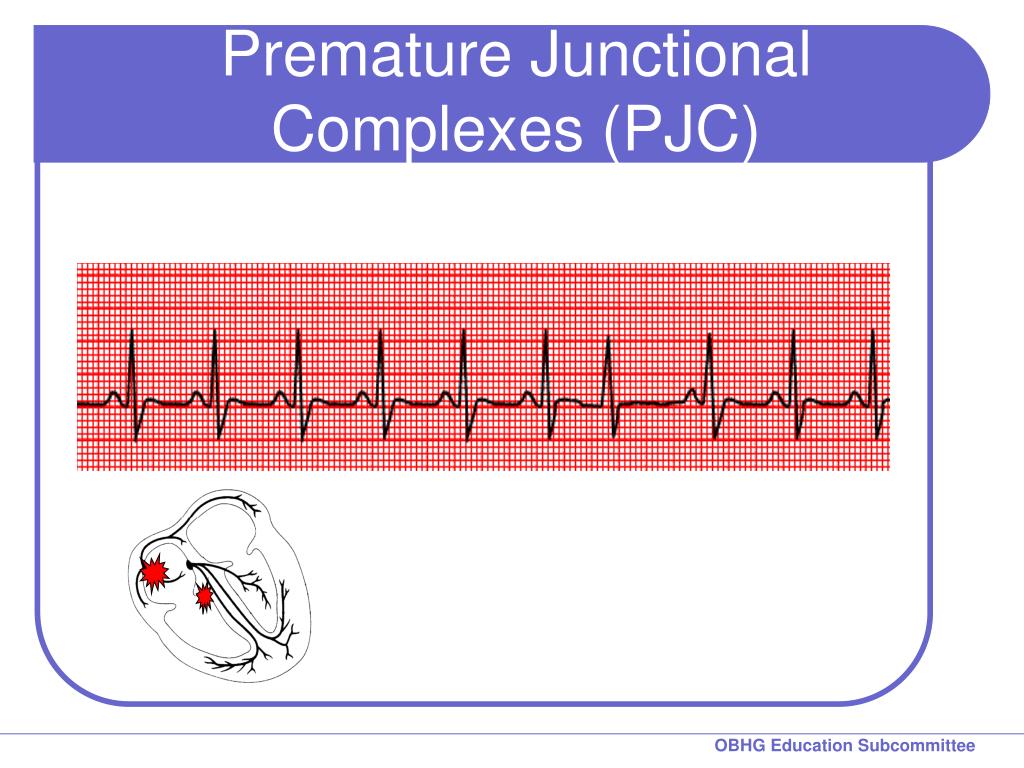



Ppt Chapter 2 For 12 Lead Training Rhythm Practice Powerpoint Presentation Id 7424




Pin By Samantha Hames On Work Emergency Nursing Icu Nursing Critical Care Nursing
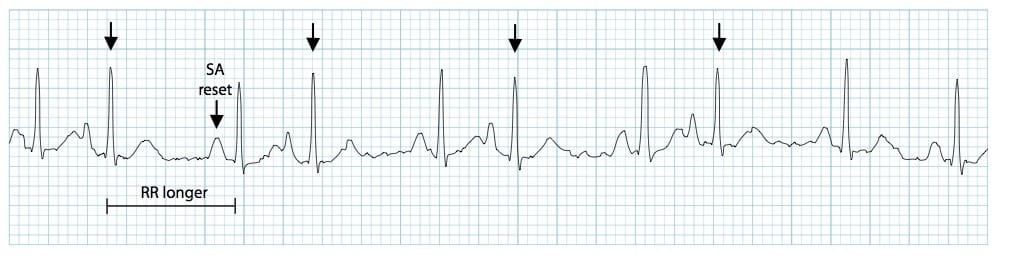



Premature Atrial Complex Pac Litfl Ecg Library Diagnosis
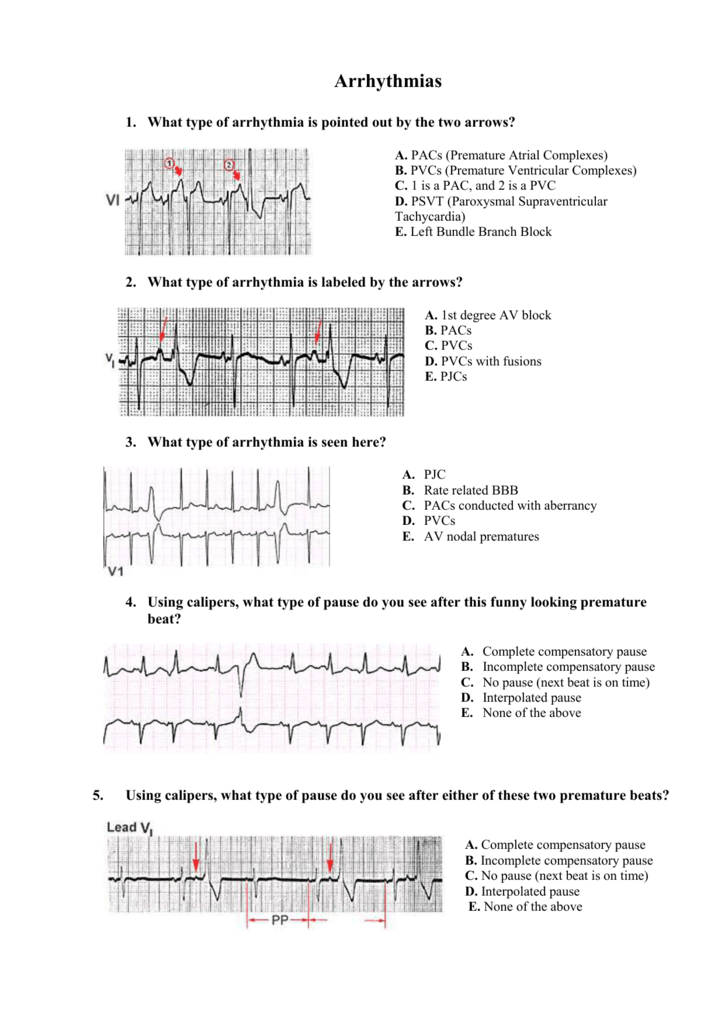



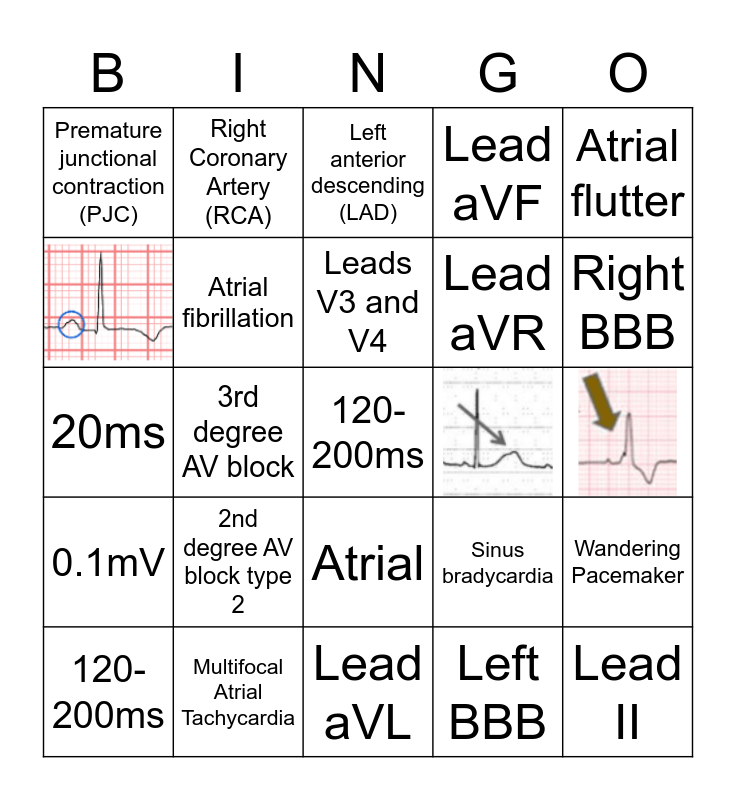
What Type Of Arrhythmia Is Pointed Out By The Two Arrows
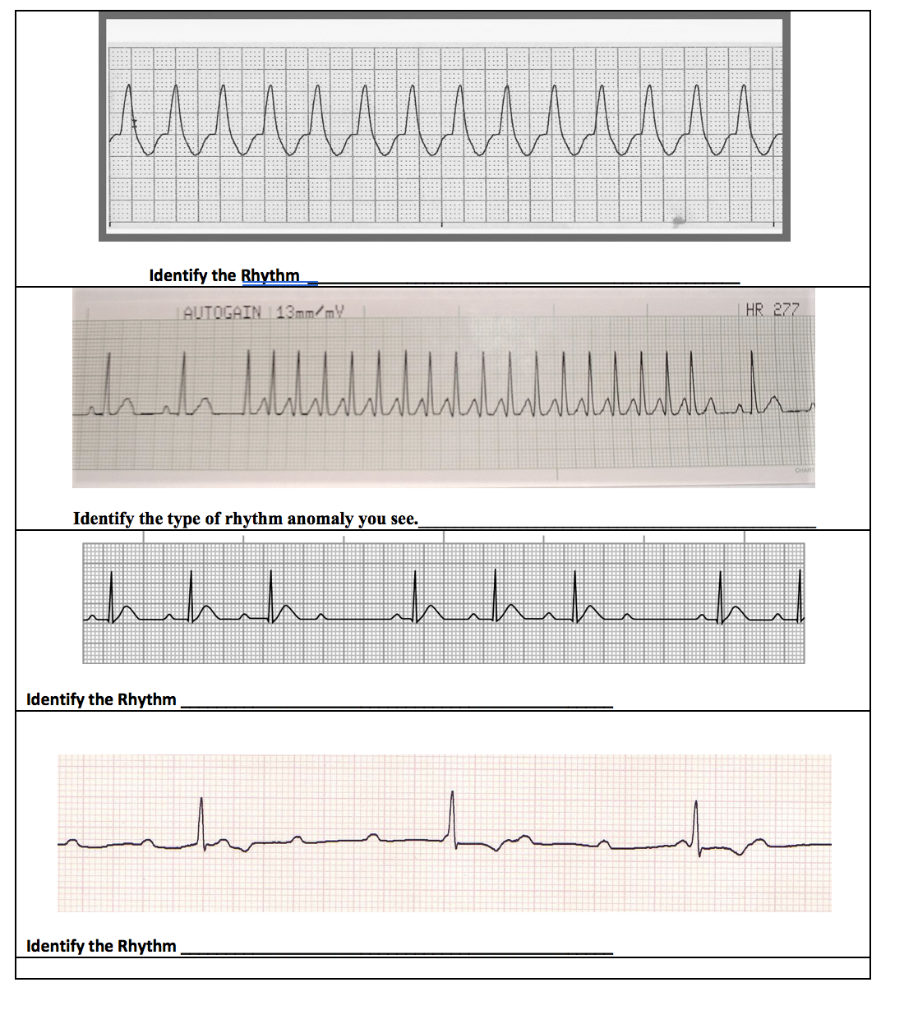



Only Use The Options Provided Answers May Be Used Chegg Com




Float Nurse Ekg Quiz 336
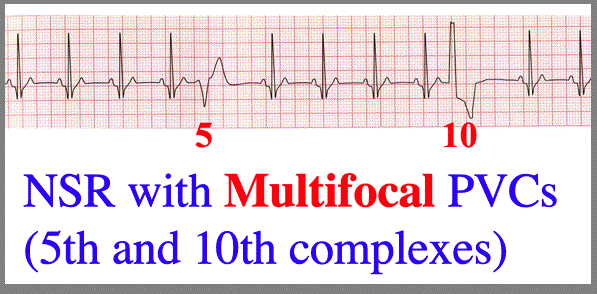



More Pvc Configurations




Pdf Arrhythmias In Children And Young Adults



Basic Electrocardiography Guide To Diagnostic Tests



2
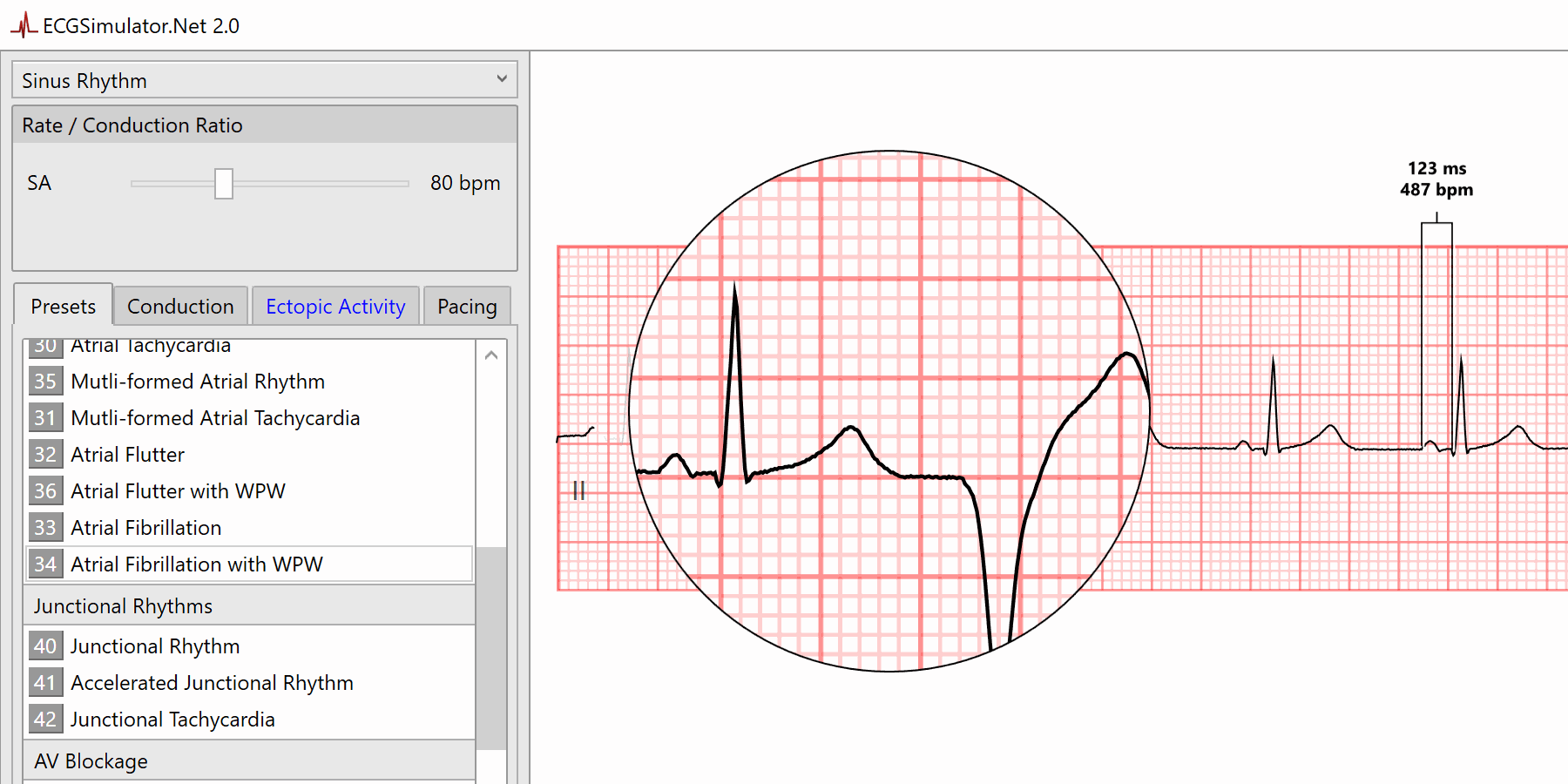



Keyboard Shortcuts Ecgsimulator Net


コメント
コメントを投稿